Do you like the Ship Page updates?We need your opinion – are these changes we've made to these pages an improvement?
Want to hide ads?
Become a Supporting Member
Become a Supporting Member
Tech Tree
European DestroyersII Romulus
III Klas Horn
IV Visby
V Västerås
VI Skåne
VII Östergötland
VIII Småland
Overview
Jump to
26Builds Submitted
1Review Submitted
23Records Submitted
Sep 2023Added to WoWS Builds
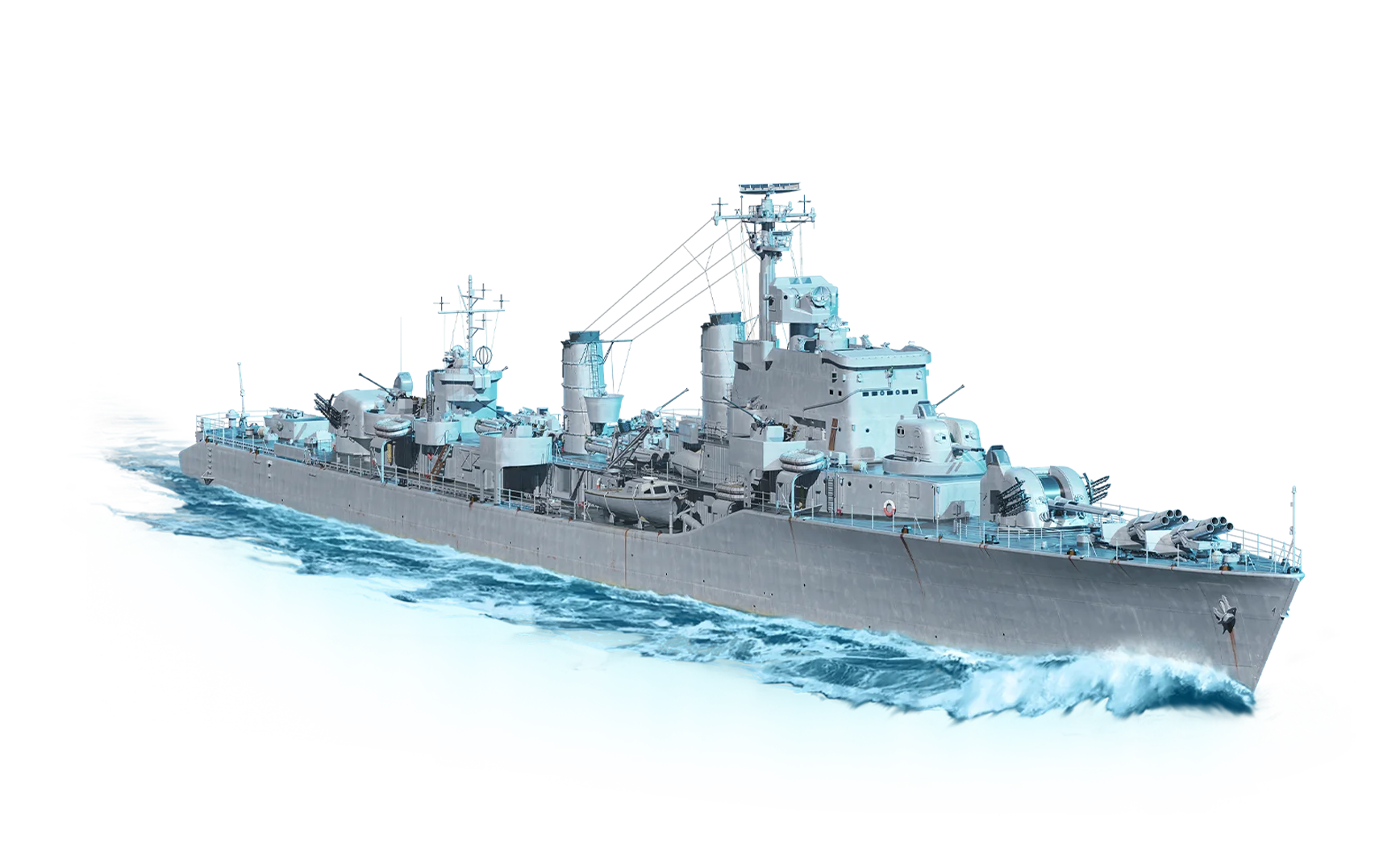
Overview of the European Destroyer Halland
The Halland-class destroyers were a series of two ships that were built for the Swedish Navy in the post-World War II era. The lead ship, named Halland, and her sister ship, Småland, were part of a naval expansion that sought to provide Sweden with a mo...
Halland Stats
Survivability
Armament
Air Defense
Maneuverability
Detectability
Halland Records
damage326757
Goldenmoon26931
Jan 2024damage311458
Tannenberg_ramm
Jan 2024damage301714
Sochi7859
Feb 2025damage255890
XdPsychotic
Jun 2025damage254339
THN642
Jan 2024damage240590
veschonblom@gmail.com
Dec 2025damage233418
hysteREKTumy
Dec 2023damage226689
Mightyfoz1067
Nov 2023damage223259
HorizontalKafka
Nov 2025damage214881
Mightyfoz1067
Nov 2023Halland Reviews
Power4.00
Fun3.00
Learning Curve3.00
Skill Ceiling4.00
Utility3.00
Konwacht
Power4
Fun3
Learning Curve3
Skill Ceiling4
Utility3
Peer Comparison
Legendary DestroyersHalland Builds
Community submitted commander builds1
HallandEvamorita36
Feb 20241
Buildmorningsunkiller666
Mar 20241
Torpedo hallandmorningsunkiller666
Mar 20241
BuildSirkillslots5743
Feb 20241
Plane Slayermorningsunkiller666
Jun 20241
aa buildepsilon105
Oct 20251
Ninja HallandSusurrador93
Feb 20241
Hybrid HallandCherrybird
Nov 20251
HallandDonaldTrump
Jun 20241
Concealment and torpedoesTheHystoryFleet
Dec 2023Halland Consumables
Slot 1
Damage Control Party
- Charges
- ∞
- Cooldown
- 40 s
- Duration
- 5 s
Slot 2
Engine Boost
- Charges
- 2
- Cooldown
- 180 s
- Duration
- 120 s
- Speed Boost
- 8%
Slot 3
Repair Party
- Charges
- 2
- Cooldown
- 120 s
- Duration
- 14 s
- Health per second
- 1.00%
Slot 4
Defensive AA Fire
- Charges
- 2
- Cooldown
- 150 s
- Duration
- 40 s
- AA Damage Boost
- 200%
Want to hide ads?
Become a Supporting Member
Become a Supporting Member
Want to hide ads?
Become a Supporting Member
Become a Supporting Member